Ball mill
Ball mill belongs to the group of gravity mills. Balls of different diameters act as grinding medium. They are made from high density and low grindability materials. The most commonly used grinding mediums are steel and ceramic, but for the purposes of e.g. pyrotechnics mediums made of non-sparking materials, like lead with antimony, are used.
Spis treści
Application of ball mills
Ball mills are used for grinding wet and dry, medium-hard and soft materials, continuously and periodically. They are applied in various branches of industry:
• mining industry (in ore processing),
• cement industry,
• ceramic industry,
• energy industry (in coal dust combustion and in preparing sorbent for flue gas desulfurization system).
Mills of this type work in closed as well as in open cycle. During grinding they can simultaneously dry or roast the material inside the mill. Ball mills also apply in lab scale. Production of pyrotechnic materials, where mediums made of suitable alloys preventing grinded material from exploding in grinding chamber must be used, is an example of such application.
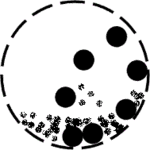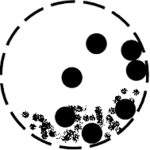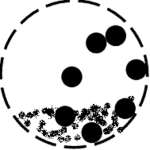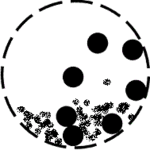
Working principle of ball mills
Working principle of ball mills is floating mediums and material under the influence of centrifugal force, caused by tumbler rotation, to the certain height. Next they fall or slide past each other grinding material by means of impact and attrition.
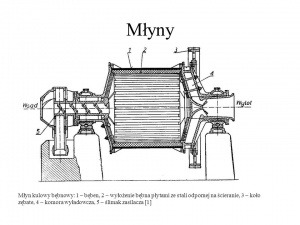
Construction of ball mill
Ball mill consists of steel tumbler with horizontal axis ended with walls shaped as cones with large opening angle. Cones are ended with spigots with an inlet axial hole on one side and an outlet on the other. Spigots are mounted in thrust roller bearings supported by strip footing. Tumbler’s diameter reaches values up to few metres, and the length from few to several dozen. Outer surface of tumblers shell is usually covered with heat covering, and its inside is lined with friction plates made from cast steel, manganese steel, and sometimes from basalt. Tumbler is filled with load of manganese steel balls. Total mass of the balls inside the tumbler depends on grinding efficiency. Powered via bevel gears transmission tumbler rotates around its horizontal axis. Feed is fed with inlet connection pipe, and carrier of grinded material suspension can be either hot air with the large addition of non-flammable and non-explosive gases like nitrogen and carbon dioxide, or flue gases from steam generator. Carrier of grinded feed flows through connection pipe.
Bibliography:
dr hab. inż. Jan Sidor prof. AGH - Lectures